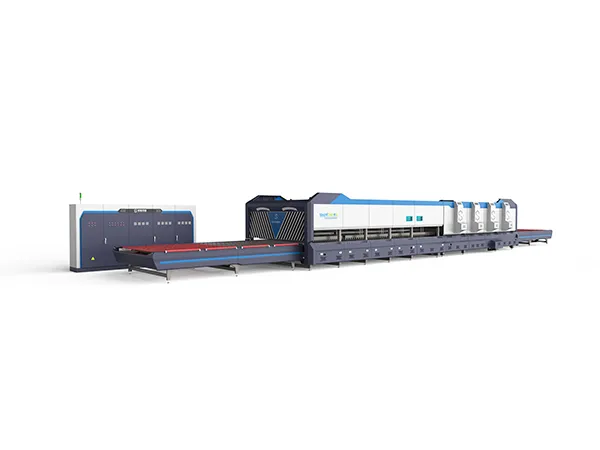
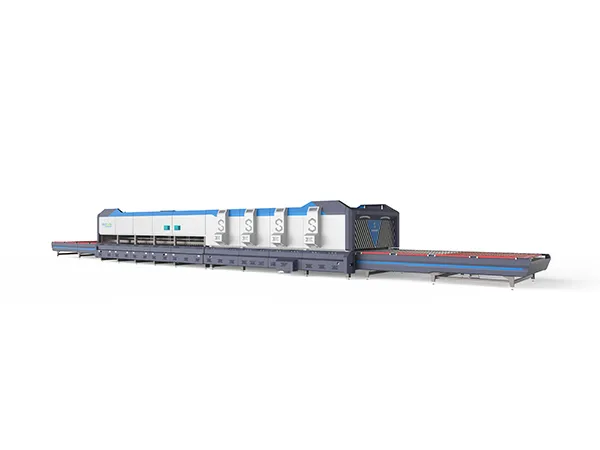
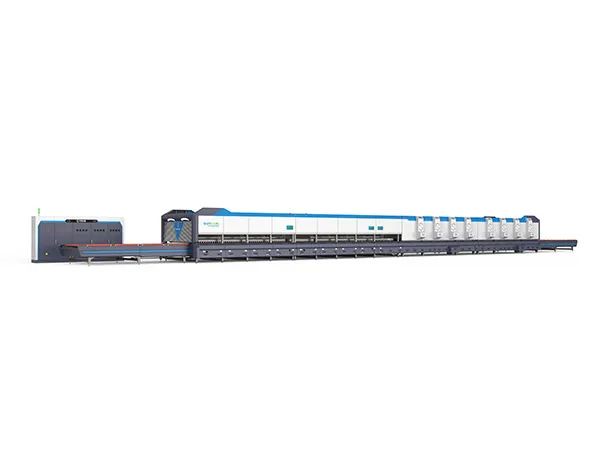
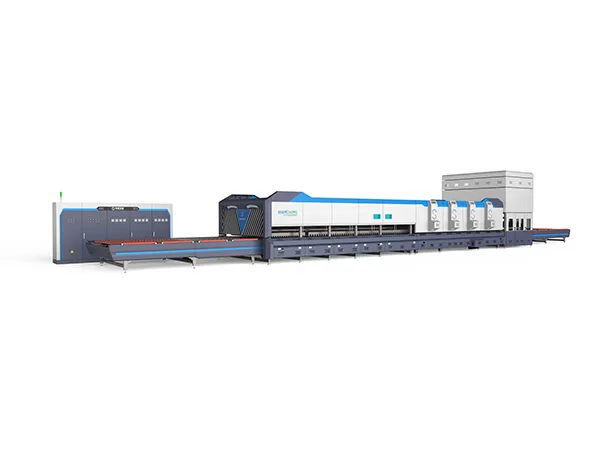
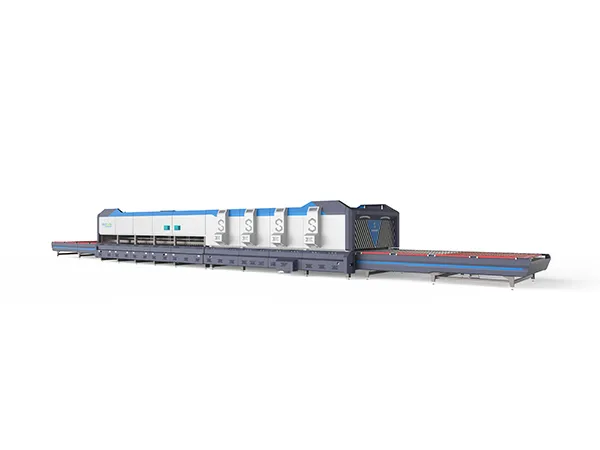
High-end, high-stress fireproof tempering furnaces are critical equipment in various industries where materials need to undergo heat treatment processes such as tempering, annealing, or stress relieving at extremely high temperatures while maintaining structural integrity and safety. These furnaces are typically used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, defense, and manufacturing of specialized components like turbine blades, gears, bearings, and tools.

Detailed Description
|
Shencheng Z Series Intelligent Type Configuration Description Table
Intelligent tailor-made, system intelligence, process datatization, parameter system optimization, productive maintenance automation and intelligence
|
|
NO.
|
Optional Functions
|
Advantage
|
|
1
|
Double belt orthogonal drive
|
Strengthen the stability of glass movement to avoid the risk of belt broken
|
|
2
|
Maintenance automatic diagnosticreminder function
|
Automatic diagnosis and reminder of daily, weekly, monthly, annual cycle maintenance items to avoid big loss caused by long- term no inspection and no maintenance
|
|
3
|
Automatic power supply protection function in case of power off( Optional )
|
In case of sudden power off during production, the system will automatically switch to the standby power supply, automatically glass exiting and rocking furnace protection to avoid greater losses.
|
|
4
|
One-click operation function
|
Storage and optimization of process and big data. One-click input system automatically matches the preferred process parameters, to avoid loss caused by inexperienoed operators or careless input of inaccurate parameters.
|
|
5
|
Automatic glass fragments cleaning function ( Optional )
|
To solve the problem of poor glass flatness caused by lower quench improper ventilation which is the result of not cleaning of glass fragments regularly by some customers.
|
|
6
|
Drive servo control ( Optional )
|
The system transmission stability is more reliable and accurate.
|
|
7
|
Ladder-type ceramic roller table
|
No gap on both sides, better insulation performance.
|
|
8
|
Stepped dual temperature control mode
|
Targeted heating make more uniform insulation and energy saving.
|
High Temperature Capability: The furnace should be capable of reaching extremely high temperatures, typically above 1000°C (1832°F), depending on the material being processed.
Uniform Heating: It's important for the furnace to provide uniform heating throughout the entire chamber to ensure consistent material properties.
Controlled Cooling: The ability to control the cooling process is essential for achieving desired material characteristics, such as hardness, strength, or resilience. This often involves precise regulation of cooling rates.
Fireproof Construction: Given the extreme temperatures involved, the furnace must be constructed from fireproof materials capable of withstanding prolonged exposure to high heat without deformation or damage.
Refractory Lining: Inside the furnace, there should be a refractory lining designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock. This lining helps to maintain the integrity of the furnace structure and provides insulation.
Automation and Control Systems: Modern high-end furnaces often feature advanced automation and control systems, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) for precise control over temperature profiles and process parameters.
Safety Features: Safety is paramount in high-temperature industrial processes. The furnace should be equipped with safety features such as temperature sensors, overheat protection, and emergency shut-off systems to prevent accidents and equipment damage.
Energy Efficiency: While high-temperature processes inherently require a significant amount of energy, a high-quality furnace should incorporate energy-efficient design features where possible to minimize operational costs and environmental impact.
Size and Capacity: The size and capacity of the furnace should be chosen based on the specific needs of the application, including the size and quantity of the materials being processed.
Reliability and Maintenance: A high-end furnace should be designed for reliability and ease of maintenance to minimize downtime and ensure consistent performance over time.
Aerospace Industry: In aerospace manufacturing, components like turbine blades, engine parts, and structural components require precise heat treatment to ensure they can withstand extreme conditions during flight. High-stress fireproof tempering furnaces are used to temper these components, enhancing their mechanical properties, durability, and resistance to fatigue.
Automotive Industry: In automotive manufacturing, various components such as engine valves, crankshafts, and gears undergo heat treatment processes to improve their strength, hardness, and wear resistance. High-end tempering furnaces play a crucial role in achieving the desired metallurgical properties in these components, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of automotive parts.
Defense Industry: The defense industry relies on high-performance materials for the production of military-grade equipment and weaponry. Fireproof tempering furnaces are used to heat treat components such as armor plates, gun barrels, and missile components to enhance their hardness, toughness, and resistance to extreme conditions encountered in combat situations.
Tool and Die Manufacturing: Tools and dies used in metalworking, plastic injection molding, and forging processes undergo heat treatment to improve their wear resistance, hardness, and dimensional stability. High-stress fireproof tempering furnaces are utilized to precisely control the heating and cooling processes, ensuring the desired metallurgical properties are achieved in these critical manufacturing tools.
Specialized Manufacturing: Various specialized industries such as medical device manufacturing, semiconductor production, and precision engineering also rely on high-end tempering furnaces for heat treatment processes tailored to their specific requirements. These furnaces are used to temper components like surgical instruments, semiconductor wafers, and precision machine parts to meet stringent quality standards and performance criteria.