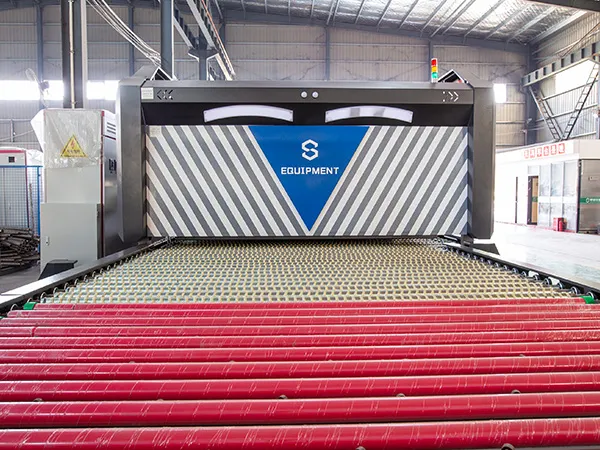
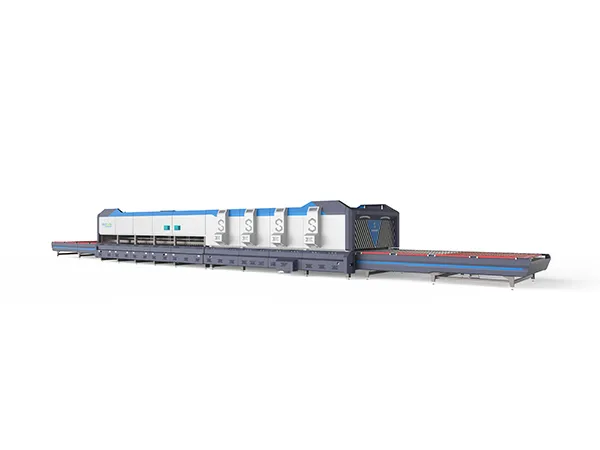
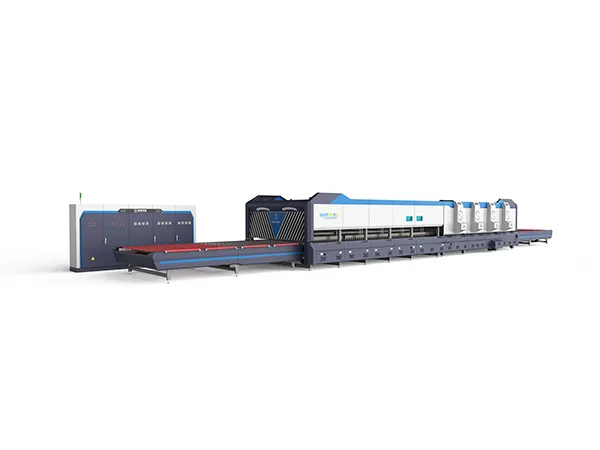
A flat glass tempering furnace is a specialized industrial machine used to heat and cool flat glass sheets in a controlled manner, enhancing their strength and safety properties. Here’s an overview of the process and key features:
Overview of the Tempering Process

Heating:
The glass sheets are heated to a temperature of approximately 620-680 degrees Celsius (1148-1256 degrees Fahrenheit), which is near the glass's softening point.
The heating is done uniformly to ensure even temperature distribution across the entire glass sheet.
Quenching:
After reaching the desired temperature, the glass is rapidly cooled using high-pressure air jets.
The rapid cooling causes the surface of the glass to solidify quickly while the interior remains slightly warmer and more fluid for a short time.
This process creates compressive stresses on the surface and tensile stresses in the interior, giving the tempered glass its strength.
Key Features of a Flat Glass Tempering Furnace

Heating Section:
Usually consists of electric heating elements or gas burners.
Equipped with precise temperature control systems to maintain uniform heating.
Quenching Section:
Comprises a series of air nozzles that blow high-pressure air onto the heated glass.
Designed to cool the glass rapidly and uniformly.
Conveyor System:
Transports the glass sheets through the heating and quenching sections.
Made of materials that can withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Control System:
Advanced computer systems control the entire process, ensuring precise temperature management and air flow.
Often includes sensors and feedback mechanisms to monitor and adjust parameters in real time.
Safety Features:
Safety interlocks and emergency shutdown systems.
Protective barriers and insulation to prevent accidental contact with hot surfaces.
Applications
Architectural Glass: Used in buildings for windows, facades, and glass doors.
Automotive Glass: Windshields, side windows, and rear windows.
Furniture and Appliances: Glass tops for tables, shelves, and doors for appliances like ovens and refrigerators.
Advantages of Tempered Glass

Increased Strength: Tempered glass is approximately four to five times stronger than standard annealed glass.
Safety: When broken, it shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury.
Thermal Resistance: Better withstands thermal stresses and temperature variations.
Considerations
Size Limitations: The size of the furnace determines the maximum dimensions of the glass that can be tempered.
Edge and Surface Quality: Proper handling and processing are crucial to maintaining the quality and strength of the tempered glass.
Overall, flat glass tempering furnaces are essential for producing high-strength, safe glass products used in various industries.